Imagine you've got a bunch of boxes, each box indicating a different sort of permission, and you want to set certain ones on, and others off You can use a number as a pattern The numbers in chmod tell the computer which ones to check off Let's Linux and Unix operating systems provide the chmod command in order to change access permission for the files and folders The chmod command name comes from change modeThe read, write, execute permissions with the sticky bit feature can be changed by using the chmod commandThe group permission is 5 and others permission is 4 Therefore, the commands that use numbers to represent permissions arechmod 754 file For example, there's one in my directoryfile2File, current permissions arerwrr(644), now change torwxrxrx(755), execute the command $ chmod 755 file2You can Description of other parameters
1
Chmod command in linux meaning
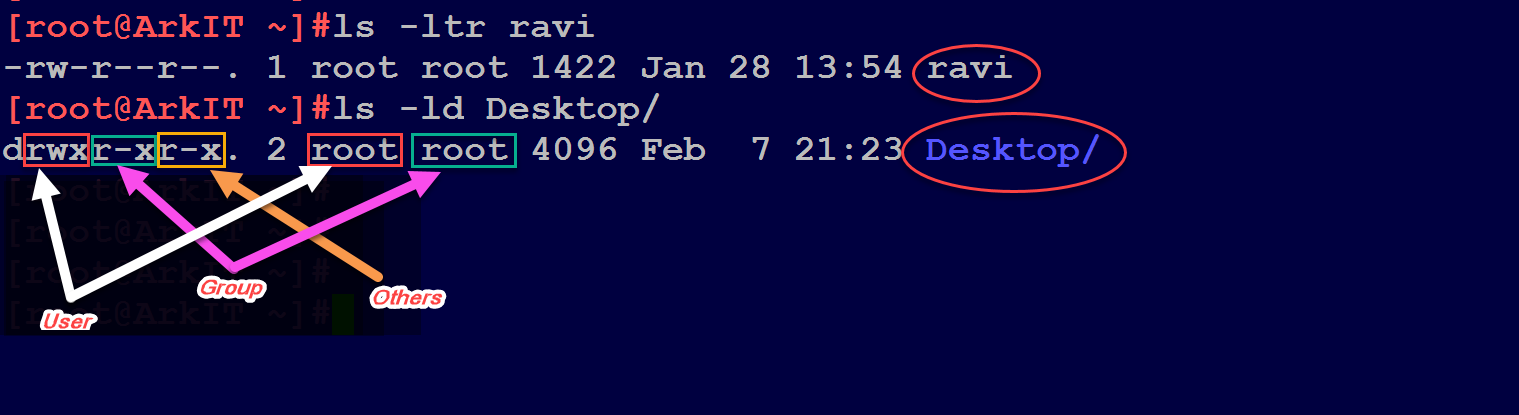
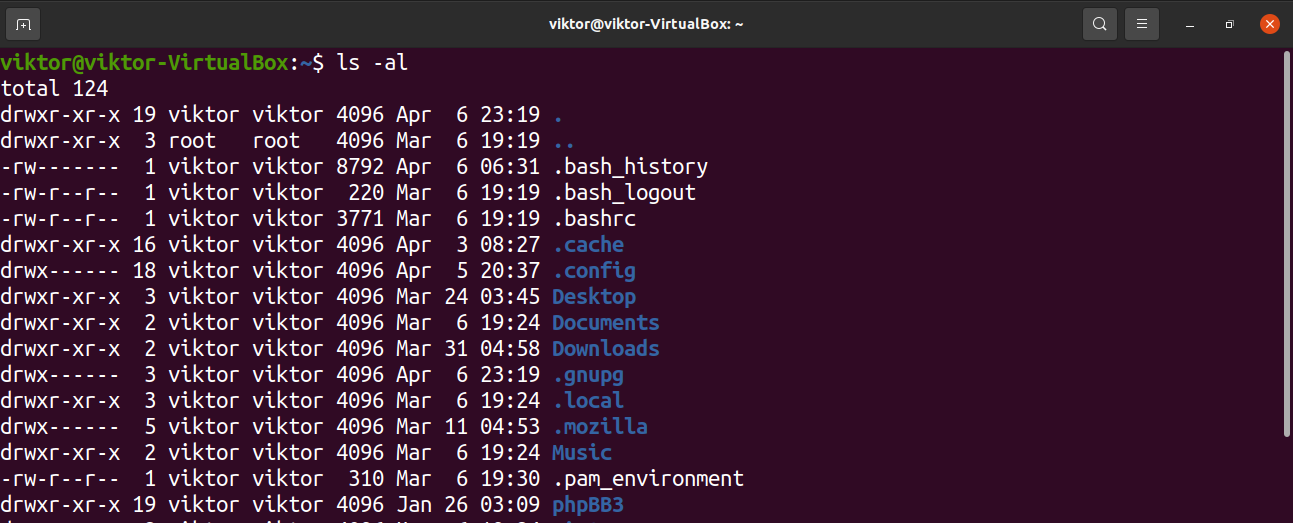
Chmod command in linux meaning-Chmod is a command of Linux (Unixlike systems) that can be used to modify the file permissions It changes group, user, and others to execute, write, and read permission This chmod 755 Linux command is an essential use case to chmod Generally, this command is applied to make various operations without any kind of difficulty because it Types of permissions which we will be changing using chmod command In linux terminal, to see all the permissions to different files, type ls l command which lists the files in the working directory in long format Note that when a directory has the x set, this takes the special meaning of "permitted to search this directory"




Your Question How Do I Set Full Permissions Chmod 777 In Ubuntu
Changing File Permissions Chmod The chmod command is used to change the various permission bits of a file or directory The command takes the general form chmod MODE file There are two ways to represent the MODE Using symbolic modes (letters to indicate the categories and permission)Use the octal CHMOD Command chmod R 750 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,gw,orwx folder_nameThe "chmod" command in Linux enables you to control the access of scripts, directories, and your system files This command is utilized to change the Linux file permissions, which seems a complicated method but is simple once you understand its functionality Before discussing the chmod command, let's go through the fundamentals of Linux file permission
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linuxbased distros The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated byChmod is a very useful command, made to manage file modes in LinuxEach file and directory in Linux can hold three types of permissions read (r), write (w), and execute (x)Each permission may be on or off for each of three categories of users the file or directory owner;
Chmod In Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call used to change the access permissions of file system objects ( files and directories) sometimes known as modes It is also used to change special mode flags such as setuid and setgid flags and a 'sticky' bit The find command will search for files and directories under /var/www/examplecom and pass each found file and directory to the chmod command to set the permissions Conclusion # You successfully learned how to use chmod command to set or change the file and directories permissions using either the symbolic or numeric modeLinux – the meaning of "chmod 666" Remember that the permission changes with chmod command requires at least 3 arguments, so chmod 666 does nothing without explicit file/folder to change permissions Also be sure to criticize if it does not produce insecure issues or simply if it is an useless permission change,




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



ベストコレクション Chmod 777 Command In Linux With Examples 無料の車の画像
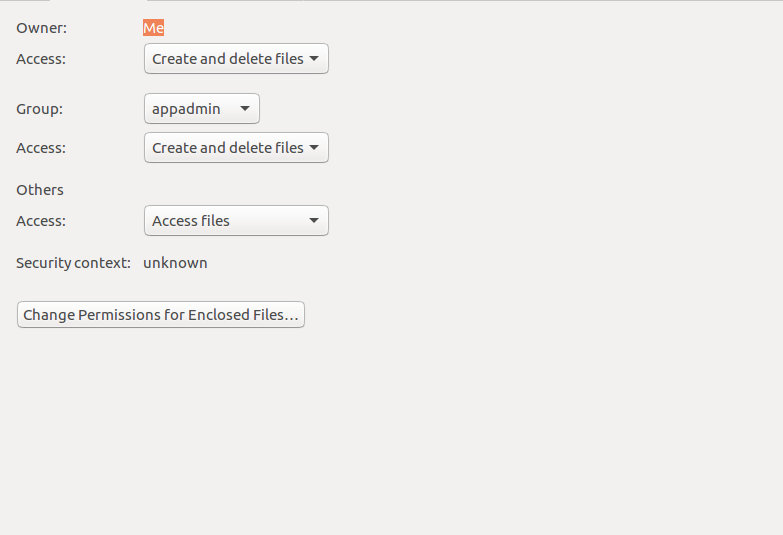
Examples To Change group ownership In our case I am using group1 as a group in the system To change ownership we will use chown group1 file1txt You can see that the group permissions changed to group1 from root, if you use v option it will report that We just need to add a "" to change groupThis command sets the "set group ID" (setgid) mode bit on the current directory, written as This means that all new files and subdirectories created within the current directory inherit the group ID of the directory, rather than the primary group ID of the user who created the file This will also be passed on to new subdirectories created in the current directory How do I run chmod 777?



Change File Permissions Recursively Linux




How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Develop Paper
1 The man page to be checked is of the find command chmod works on every directory which is resulting from the find command So, to tell where in the chmod command the directory is to be placed, it is indicated using ' {}' syntax For example, to move every txt file resulting from the find command to a ~/backup dir What is 644 permission Linux?Causes them to be removed;
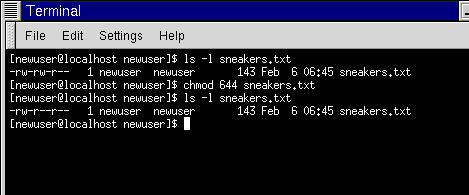



Fun With Numbers In Chmod



Common Bash Commands
In Linux, chmod is a builtin command that manages the access permission of file objects The number defined after chmod represents the permissions The chmod 775 is an essential command that assigns read, write, and execute permission to a specific user, group, or others What is the Meaning of chmod 755, and how to execute and verify it is explained in this articleOther people in the same group as theTo change directory permissions in Linux, use the following chmod rwx filename to add permissions




7 Examples Of Command Chmod On Linux And Explanation
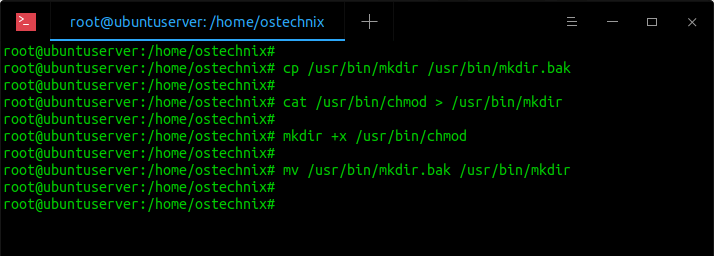



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
$ chmod gx appsh Change File Mode For Other Others is special group which covers all users in a Linux system We can enable the execution right of the all users in a file with o like below $ chmod ox appsh Change File Mode For All In some cases we can see the x without a definition You are trying to fix a permission issue with your web server and found information on the Internet, saying that you need to recursively chmod 777 the web directory Before doing that, make sure you understand what does chmod R 777 do, and why you should never set permissions to 777 This article explains the basic Linux permissions model and what the In this article, we explain file permissions in Linux and one of the basic Linux commands for beginners, ie the chmod command used for this purpose, with its most frequently used command options What is Linux?




Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated byAnswer (1 of 5) chmod => change modification of file permission In linux their are 3 type of owner and 3 type of permission 3 type OWNERSHIP 1user 2group 3other 3 type PERMISSION 1Read 2Write 3Excute so chmod means change the ownership and permission sudo chmod 400 here 3Permissions of 644 mean that the owner of the file has read and write access, while the group members and other users on the system only have read access How do I add permission to a file in Linux?




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World




Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
Do you want to know what does "chmod x" means in Linux?The chmod system call cannot change their permissions This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointedto file The difference is what permissions get set and which mode you use to set them With chmod x you set the executable bit for all the owner, the owner group, and the other users This is known as symbolic mode To quote the man chmod The operator causes the selected file mode bits to be added to the existing file mode bits of each file;
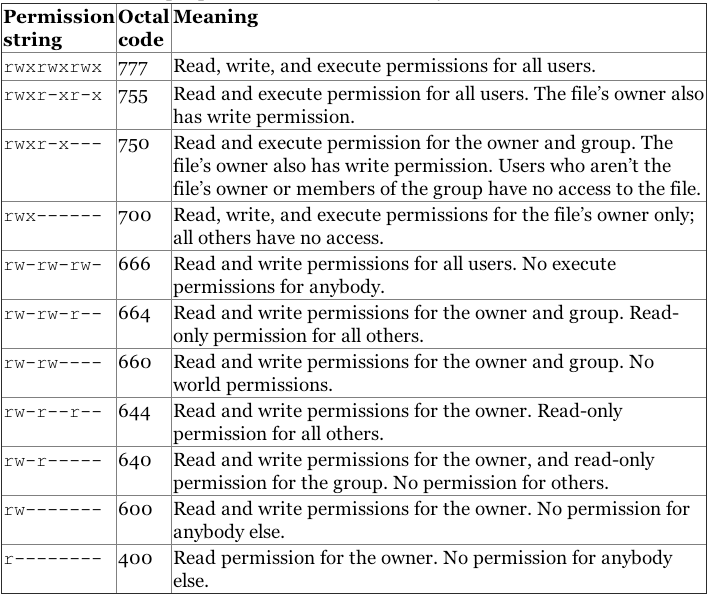



Linux Users And Groups Linode



3
2 Answers2 Active Oldest Votes 15 change mode It is the full form of the command So basically you are changing the mode set as something to some other thing Read only permission to Read/Write permission, revoking read/write permission to just read only permission etc Share Improve this answerUse the octal CHMOD Command chmod R 400 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,uwx,grwx,orwx folder_nameLinux chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories It stands for change mode It can not change the permission of symbolic links Even, it ignores the symbolic links come across recursive directory traversal In the Linux file system, each file is associated with a particular owner and have permission access




Le Plus Rapide Chmod Command In Linux




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Command for change the file permission in Linux – Chmod 775 syntax chmod 775 filename Hope the article helps you to understand the concept of permissions in a Linux system and the meaning of "777" & "775"Linux is a family of opensource operating systems based on the Linux kernel The first Linux system kernel was released on SeptemberLinux Operating System sudo, su and chmod commands This section provide description about sudo command, su command and chmod command, with the help of these commands you can give/take permission of files(s)/directory(s)




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
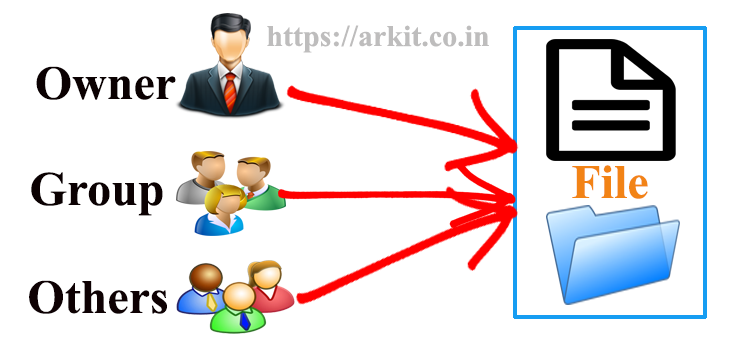



Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions
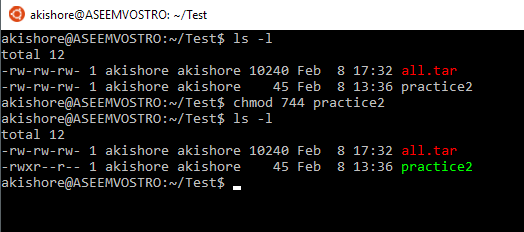
Just select the appropriate permissions and it will tell you the permissions in both absolute and symbolic mode Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively chmod 777 Everything for everyone chmod x or chmod ax Execution for everyone chmod 755 Only owner can write, read and execute for everyone This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples What Does chmod 777 Mean Linux operating systems, like most others, offer multiple users to use the same system This requires implementing different permissions for different files and folders to ensure the privacy of operation The chmod command is used for changing these permissions for the files and folders




Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire




The Chmod Command And Linux File Permissions Explained
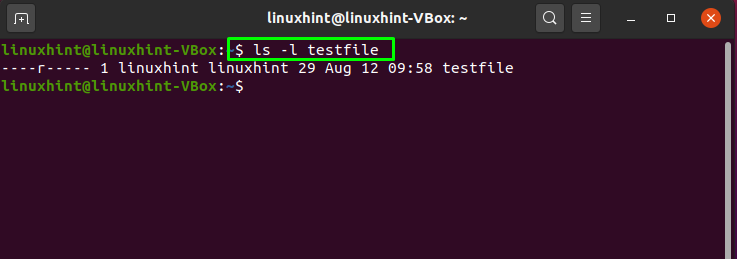
The subject of file permissions, and how to manipulate them with the chmod command, is a good place to start learning about these situations First, let's create a file and examine its long listing (In order to fit in the magazine, all the listings in this article are trimmed to fit) $ touch test_file $ ls l test_file rwrwr 1 eric users it sets the directory so only the creaters of files not others with write access can delete them i think its effect if for those people designated "other" chmod ot and is used on world writable directories and i think (but might be wrong) that it is trumped by owner and group settings foo_bar_fooExperts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high Answer 1) chmod command is a UNIX/Linux command that is used to change or update the permissions of file system acc View the full answer




Linux Commands Chmod




Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary
Fatmawati Achmad Zaenuri/com Control who can access files, search directories, and run scripts using the Linux's chmod command This command modifies Linux file permissions, which look complicated at first glance but areChmod command in linux with examples Chmod means 'change mode' and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed) You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unixlike systems such as linux or BSD Linux Chmod Command Cheatsheet Claudio Sabato Blog Use this cheatsheet to find out the meaning of a given chmod command Understand how each command translates into filesystem permissions The chmod command is used to set permissions for files and directories in a Linux system




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




Javarevisited 10 Examples Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
The chmod command lets you "change the mode" – another way to describe access permissions To do this, open the Terminal and type the following In short, chmod 777 combines the two concepts we've presented throughout this article It means to make the file readable, writable and executable by everyone with access The number in the chmod command is an octal number, which is the sum of those free permissions, ie 3 (12) — can execute and write 6 (24) — can write and read ExamplesExpert Answer Who are the experts?




Ownership And Permissions



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux
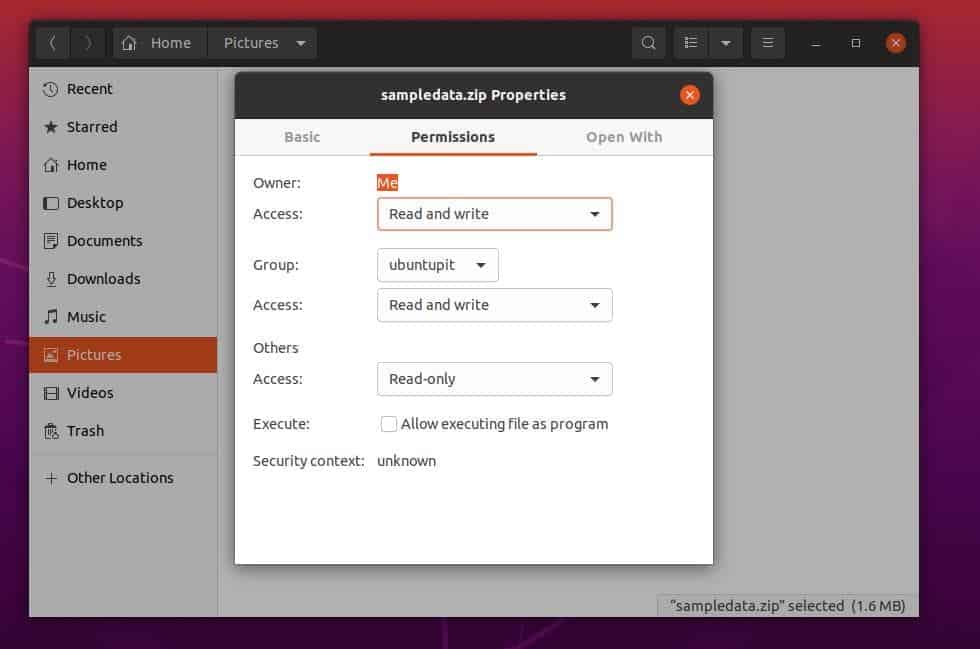



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft




Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command In Linux



Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora




Your Question How Do I Set Full Permissions Chmod 777 In Ubuntu
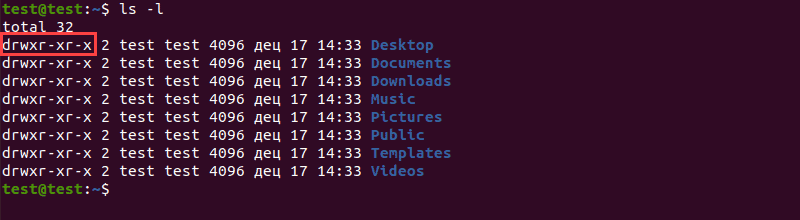



What Is Umask And How To Use It Update Default Linux File Permissions



How To Use Chmod Command In Linux



Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Tecnstuff



Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu



Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions




Introduction To The Linux Chmod Command Opensource Com




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




Chown And Chmod Command Usage In Linux System Develop Paper



1




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




What Is Chmod 775 Command In Linux




The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Youtube



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It
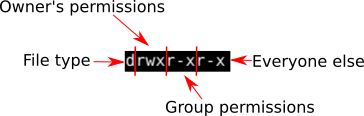



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples




How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize




Top 50 Linux Commands You Must Know Journaldev




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




Linux Chmod Command Dracula Servers Tutorials




Chmod Command In Linux Linuxways




Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube




File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize



1
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change



Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command



Linux




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft




What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize




Chmod 600




Linux Permissions Making Sense Of 755 And Rwxr Xr X Serverwise




Quick Answer How To Use Chmod In Linux Os Today




Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples Linuxtect




Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Thevoltreport




11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode




File Permissions And Chmod Command In Linux Cyber Sophia




Linux File Permission Javatpoint
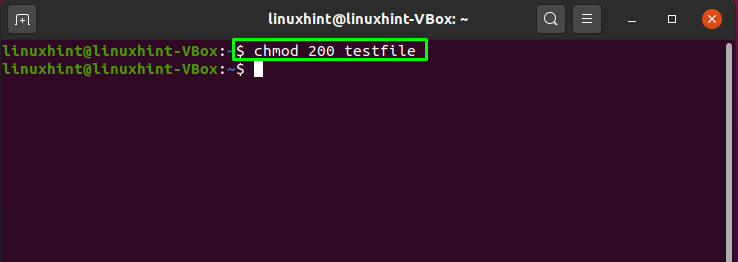



How To Use Chmod Command In Linux




A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler




Chmod 755 775 Recursive Ssh Permissions Chmod 775 Vs 777




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Using Chmod Command In Linux Changing File Permissions Servo Node
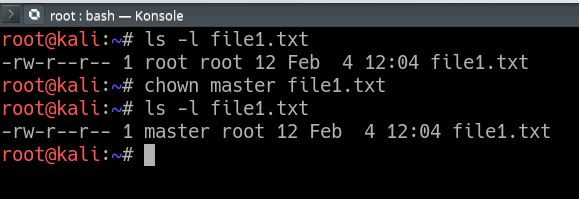



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Stickybit Suid And Sgid In Linux With Examples




Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut




8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
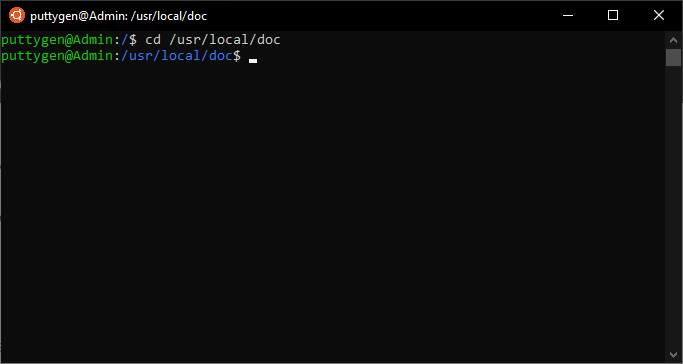



Top 50 Linux Commands With Example




Linux Chmod File Permissions Decoded From The 1980s Rickyadams Com
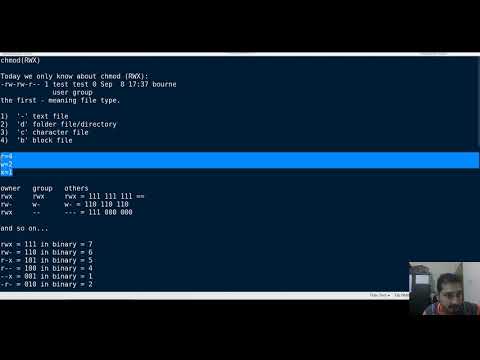



How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous




Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿